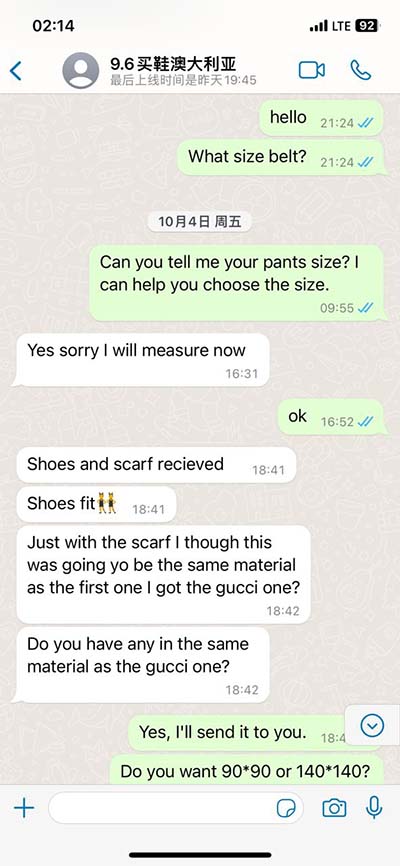
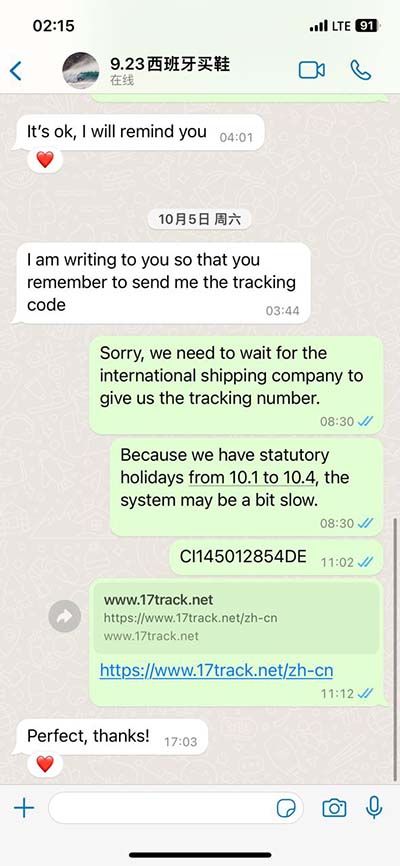
lv non-compaction cardiomyopathy | left ventricular noncompaction prognosis lv non-compaction cardiomyopathy Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC, also known as noncompaction cardiomyopathy [1]) is a complex myocardial disorder with a distinct phenotype characterized by prominent LV trabeculae and deep intertrabecular recesses [2,3]. The Louis Vuitton monogram was first introduced in 1896 as a way to combat counterfeiting and protect the brand's designs. Created by Georges Vuitton, the son of Louis Vuitton, the monogram combined the initials "LV" with various floral and geometric motifs inspired by Japanese and Art Nouveau influences.2 min read. Florida A&M University ‘s marching band, affectionately known as the Marching 100, recently brought their HBCU flair to Paris Fashion Week, performing at the Louis.
0 · non compaction cardiomyopathy life expectancy
1 · non compaction cardiomyopathy guidelines
2 · lvnc life expectancy
3 · left ventricular noncompaction prognosis
4 · Lv non compaction on echo
5 · Lv non compaction guidelines
6 · Lv non compaction echo criteria
7 · Lv non compaction criteria
How to tell if Louis Vuitton is real (or fake) Bags: Check the “LOUIS VUITTON ®” inscription engraved in leather. Fake bags always have thicker text. Footwear: Verify the inscriptions on the soles. Fake shoes always have too little space in-between the text. Clothing: Look at the wash tags. A fake Louis Vuitton always has very thick prints.
non compaction cardiomyopathy life expectancy
Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) is a rare cardiomyopathy that usually affects the left ventricle in which the two-layered myocardium has an abnormally thick sponge-like, trabecular layer and a thinner, compacted myocardial layer. Left ventricular noncompaction is a rare cardiomyopathy, that should be considered as a possible diagnosis because of its potential complications – heart failure, ventricular arrhythmias, and embolic events.Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) cardiomyopathy is a condition where your lower left heart chamber (left ventricle) doesn’t develop properly. Instead of being firm and smooth, the left ventricle is spongy and thick. Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC, also known as noncompaction cardiomyopathy [1]) is a complex myocardial disorder with a distinct phenotype characterized by prominent LV trabeculae and deep intertrabecular recesses [2,3].
Left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathy (LVNC) remains a largely underinvestigated and poorly understood diagnosis. The number of peer‐reviewed articles published on LVNC has grown dramatically over the past decade. Left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathy (LVNC) is a rare congenital heart problem. It develops from faulty development of your left ventricle. The left ventricle is the main heart.
louis vuitton vintage monogram handbag
In this review, left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathy, which is often caused by mutations in sarcomere and cytoskeletal proteins and is also associated with metabolic abnormalities, is discussed.Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) is a rare congenital phenotype defined by the presence of prominent left ventricular trabeculae, deep intertrabecular recesses (continuous with the ventricular cavity), and a thin compacted layer.Non-compaction cardiomyopathy is a congenital disorder of the myocardium that causes cardiomyopathy, a variety of arrhythmias, conduction disorders, and an increased risk of sudden death. Diagnosis includes ECG, cardiac imaging, and genetic testing.Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) is a type of heart muscle disease, or cardiomyopathy, that we may diagnose after examining the heart’s main pumping chamber. While this chamber, the left ventricle, normally looks smooth, its muscle can occasionally appear spongy or “hypertrabeculated.”

Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) is a rare cardiomyopathy that usually affects the left ventricle in which the two-layered myocardium has an abnormally thick sponge-like, trabecular layer and a thinner, compacted myocardial layer. Left ventricular noncompaction is a rare cardiomyopathy, that should be considered as a possible diagnosis because of its potential complications – heart failure, ventricular arrhythmias, and embolic events.
Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) cardiomyopathy is a condition where your lower left heart chamber (left ventricle) doesn’t develop properly. Instead of being firm and smooth, the left ventricle is spongy and thick. Left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC, also known as noncompaction cardiomyopathy [1]) is a complex myocardial disorder with a distinct phenotype characterized by prominent LV trabeculae and deep intertrabecular recesses [2,3]. Left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathy (LVNC) remains a largely underinvestigated and poorly understood diagnosis. The number of peer‐reviewed articles published on LVNC has grown dramatically over the past decade. Left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathy (LVNC) is a rare congenital heart problem. It develops from faulty development of your left ventricle. The left ventricle is the main heart.
In this review, left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathy, which is often caused by mutations in sarcomere and cytoskeletal proteins and is also associated with metabolic abnormalities, is discussed.
Left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) is a rare congenital phenotype defined by the presence of prominent left ventricular trabeculae, deep intertrabecular recesses (continuous with the ventricular cavity), and a thin compacted layer.
Non-compaction cardiomyopathy is a congenital disorder of the myocardium that causes cardiomyopathy, a variety of arrhythmias, conduction disorders, and an increased risk of sudden death. Diagnosis includes ECG, cardiac imaging, and genetic testing.
non compaction cardiomyopathy guidelines
lvnc life expectancy
left ventricular noncompaction prognosis

Everything you need to know about farming Paradox Brothers efficiently! His decklists, card rewards, top level farm decks with strategy information and free to play card replacements.
lv non-compaction cardiomyopathy|left ventricular noncompaction prognosis