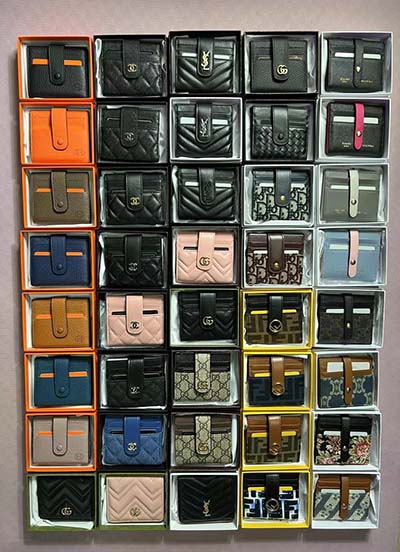
lv pressure volume curve | normal lv pressures lv pressure volume curve The first method of volume calibration relies on immediate pre-procedure measurements of LV end-diastolic volume (V ed) and stroke volume (SV) or ejection fraction .
Freedom Beat. Downtown Grand. (702) 719-5315 | Official site. Price: $25-$75. Hours: Mon-Sun, noon-3 a.m. Type: Coffee Shops - Menu. Visit Freedom Beat to enjoy classic American cuisine. The venue offers Freedom 2 Brunch every Saturday & Sunday from 10am – 2pm with live local artists and options to include bottomless mimosa or bloody .
0 · normal lv pressures
1 · normal lv pressure range
2 · normal lv filling pressure
3 · normal lv end diastolic pressure
4 · normal blood pressure chart
5 · lvedp blood pressure chart
6 · lv pressure sensor
7 · lv end diastolic pressure
Affordable Financing Solutions for Lawn and Garden Dealers and Their Customers.Professional’s first choice is this industrial grade TLV-31D featuring a 31hp Vanguard Daihatsu twin cylinder big block engine. Built to last, this product offers a heavy duty framework coupled with a replaceable blower housing liner.
EDPVR (End-Diastolic Pressure-Volume Relationship) shows the relationship between ESV and left ventricular volume. The EDPVR curve shows that the left ventricle can withstand large pressure increases but at a certain threshold, pressure rises rapidly with further volume .Ventricular filling occurs along the end-diastolic pressure-volume relationship (EDPVR), or passive filling curve for the ventricle. The slope of the EDPVR is the reciprocal of ventricular . Background: Left ventricular (LV) efficiency is a key pathophysiological marker in heart failure (HF). LV pressure curve estimation and three-dimensional (3D) volumes via .A shift of the curve to A indicates that a higher left ventricular (LV) pressure will be required to distend the LV to a similar volume, indicating that the ventricle is less distensible. The slope of .
normal lv pressures
normal lv pressure range
normal lv filling pressure
End-diastolic pressure–volume relationship concepts. (A) V30 is the left ventricular (LV) volume at a pressure of 30 mmHg and reflects compliance. A shift to the left suggests diastolic .
The first method of volume calibration relies on immediate pre-procedure measurements of LV end-diastolic volume (V ed) and stroke volume (SV) or ejection fraction . This review focuses on intra cardiac left ventricular PV analysis principles, interpretation of signals, and potential clinical applications. Keywords: Left ventricular . This pressure volume loop diagram represents the 5 phases of the cardiac cycle. It makes more sense to start at the end of stage 4 of the cardiac cycle: isovolumetric relaxation . Effects of Preload, Afterload and Inotropy on Ventricular Pressure-Volume Loops. Ventricular pressure-volume (PV) loops are an excellent tool for visualizing changes in .
EDPVR (End-Diastolic Pressure-Volume Relationship) shows the relationship between ESV and left ventricular volume. The EDPVR curve shows that the left ventricle can withstand large pressure increases but at a certain threshold, pressure rises rapidly with further volume increases.Ventricular filling occurs along the end-diastolic pressure-volume relationship (EDPVR), or passive filling curve for the ventricle. The slope of the EDPVR is the reciprocal of ventricular compliance. Therefore, changes in ventricular compliance alter the slope of .
A PV loop plots the changes in ventricular pressure associated with the changes in volume which occur during the cardiac cycle. The plot of a ventricular pressure-volume loop contains the following information: Volumes: End-diastolic volume (where the mitral valve closes) End-systolic volume (where the aortic valve closes) Background: Left ventricular (LV) efficiency is a key pathophysiological marker in heart failure (HF). LV pressure curve estimation and three-dimensional (3D) volumes via echocardiography allows for non-invasive pressure-volume (PV) analysis and calculation of an index of efficiency (Figure 1). Aim: Validate efficiency index by 3D echocardiography by .A shift of the curve to A indicates that a higher left ventricular (LV) pressure will be required to distend the LV to a similar volume, indicating that the ventricle is less distensible. The slope of the LV end-diastolic pressure-volume relation indicates the passive chamber stiffness.End-diastolic pressure–volume relationship concepts. (A) V30 is the left ventricular (LV) volume at a pressure of 30 mmHg and reflects compliance. A shift to the left suggests diastolic dysfunction (red), to the right ventricular remodelling (blue).
The first method of volume calibration relies on immediate pre-procedure measurements of LV end-diastolic volume (V ed) and stroke volume (SV) or ejection fraction (EF) taken from echocardiography, computed tomography, or cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. This review focuses on intra cardiac left ventricular PV analysis principles, interpretation of signals, and potential clinical applications. Keywords: Left ventricular haemodynamics; Myocardial energetics; Pressure-volume loop. This pressure volume loop diagram represents the 5 phases of the cardiac cycle. It makes more sense to start at the end of stage 4 of the cardiac cycle: isovolumetric relaxation and beginning of stage 5- ventricular diastole. At this point, the end systolic volume of the LV is +- . Effects of Preload, Afterload and Inotropy on Ventricular Pressure-Volume Loops. Ventricular pressure-volume (PV) loops are an excellent tool for visualizing changes in ventricular function in response to changes in preload, afterload and inotropy.
EDPVR (End-Diastolic Pressure-Volume Relationship) shows the relationship between ESV and left ventricular volume. The EDPVR curve shows that the left ventricle can withstand large pressure increases but at a certain threshold, pressure rises rapidly with further volume increases.Ventricular filling occurs along the end-diastolic pressure-volume relationship (EDPVR), or passive filling curve for the ventricle. The slope of the EDPVR is the reciprocal of ventricular compliance. Therefore, changes in ventricular compliance alter the slope of .
A PV loop plots the changes in ventricular pressure associated with the changes in volume which occur during the cardiac cycle. The plot of a ventricular pressure-volume loop contains the following information: Volumes: End-diastolic volume (where the mitral valve closes) End-systolic volume (where the aortic valve closes)
fake colonge
Background: Left ventricular (LV) efficiency is a key pathophysiological marker in heart failure (HF). LV pressure curve estimation and three-dimensional (3D) volumes via echocardiography allows for non-invasive pressure-volume (PV) analysis and calculation of an index of efficiency (Figure 1). Aim: Validate efficiency index by 3D echocardiography by .A shift of the curve to A indicates that a higher left ventricular (LV) pressure will be required to distend the LV to a similar volume, indicating that the ventricle is less distensible. The slope of the LV end-diastolic pressure-volume relation indicates the passive chamber stiffness.End-diastolic pressure–volume relationship concepts. (A) V30 is the left ventricular (LV) volume at a pressure of 30 mmHg and reflects compliance. A shift to the left suggests diastolic dysfunction (red), to the right ventricular remodelling (blue). The first method of volume calibration relies on immediate pre-procedure measurements of LV end-diastolic volume (V ed) and stroke volume (SV) or ejection fraction (EF) taken from echocardiography, computed tomography, or cardiac magnetic resonance imaging.
This review focuses on intra cardiac left ventricular PV analysis principles, interpretation of signals, and potential clinical applications. Keywords: Left ventricular haemodynamics; Myocardial energetics; Pressure-volume loop. This pressure volume loop diagram represents the 5 phases of the cardiac cycle. It makes more sense to start at the end of stage 4 of the cardiac cycle: isovolumetric relaxation and beginning of stage 5- ventricular diastole. At this point, the end systolic volume of the LV is +- .
all beauty perfume fake
oriflame perfume dupes
this is her perfume dupe
normal lv end diastolic pressure
1 Rm, 2 Guests. See All Downtown/Fremont Street Las Vegas Hotels. Overview. Full Review. Photos. Room Rates. Amenities. Map. Pros. Excellent location in the middle of Fremont Street Experience, in the heart of downtown Vegas. Reliably low room rates, plus no resort fee. Old-school on-site steakhouse, Hugo's Cellar, is a Vegas dining institution.
lv pressure volume curve|normal lv pressures