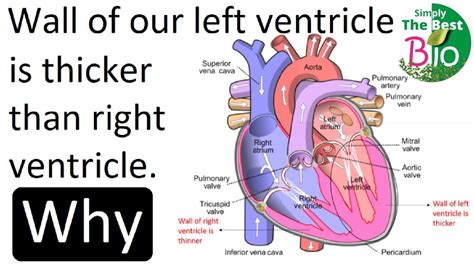
lv function of heart | what is the function and anatomy of left ventricle lv function of heart Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement, expressed as a percentage, of how much blood the left ventricle pumps out with each contraction. An ejection fraction of 60 percent . Kvalitatīva dzīves vieta Rīgas tuvumā, dažādas māju būvniecības tehnoloģijas, pilnībā izbūvētas komunikācijas, gatavi ceļi un ietves katrā ciematā, moderni apkures risinājumi. Kvalitātes garantija. Vairāk nekā 20 gadu. pieredze!
0 · why is left ventricle thicker
1 · what is the function and anatomy of left ventricle
2 · picture of left ventricle heart
3 · left ventricular hypertrophy life expectancy
4 · left ventricle receives blood from
5 · left ventricle heart diagram
6 · left ventricle function and location
7 · Lv ejection fraction chart
Continuing Contracts for Professional Services Bid Status: Unofficial: Bid Closing Date: Tue Dec 13, 2022 3:00 PM (EST) Question Deadline: . and construction phase services for capital improvements projects and other needs within the municipal limits of the City of Lake Worth Beach and/or the City’s water and electric utility service areas.
An accurate left ventricle ejection fraction (LVEF) reading can be measured through a variety of imaging techniques. The most common . The left ventricle is the thickest of the heart’s chambers and is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood to tissues all over the body. By . Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement, expressed as a percentage, of how much blood the left ventricle pumps out with each contraction. An ejection fraction of 60 percent . An accurate left ventricle ejection fraction (LVEF) reading can be measured through a variety of imaging techniques. The most common ejection fraction testing measures .
The left ventricle is the thickest of the heart’s chambers and is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood to tissues all over the body. By contrast, the right ventricle solely . Ejection fraction typically refers to the left side of the heart. It shows how much oxygen-rich blood is pumped out of the left ventricle to most of the body’s organs with each .
The left ventricle is an integral part of the cardiovascular system. Left ventricular contraction forces oxygenated blood through the aortic valve to be distributed to the entire . The left ventricle is the heart's main pumping chamber. It pumps oxygen-rich blood up into the body's main artery, called the aorta. The blood then goes to the rest of the body. .
Assessment of the size, mass, geometry, and function of the left ventricle is fundamental for the diagnosis and prognosis of most cardiac diseases, including coronary artery disease, heart . Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the central measure of left ventricular systolic function. LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in . LV GLS is useful to detect future cardiotoxicity among patients receiving cardiotoxic chemotherapy, and to detect subclinical LV systolic dysfunction among family .
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the volume of blood pumped out of the heart during systole relative to the volume in the left ventricle at the end of diastole. LVEF is calculated . Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement, expressed as a percentage, of how much blood the left ventricle pumps out with each contraction. An ejection fraction of 60 percent . An accurate left ventricle ejection fraction (LVEF) reading can be measured through a variety of imaging techniques. The most common ejection fraction testing measures .
The left ventricle is the thickest of the heart’s chambers and is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood to tissues all over the body. By contrast, the right ventricle solely . Ejection fraction typically refers to the left side of the heart. It shows how much oxygen-rich blood is pumped out of the left ventricle to most of the body’s organs with each .
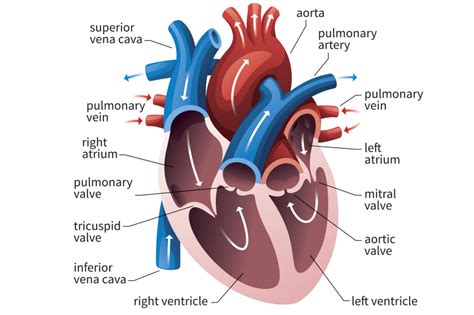
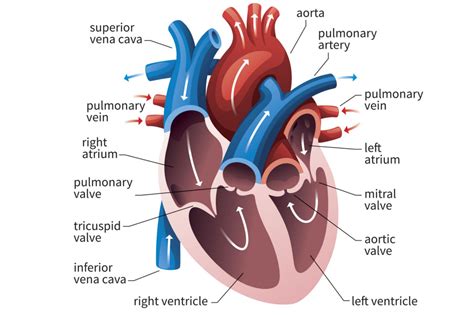
The left ventricle is an integral part of the cardiovascular system. Left ventricular contraction forces oxygenated blood through the aortic valve to be distributed to the entire .
The left ventricle is the heart's main pumping chamber. It pumps oxygen-rich blood up into the body's main artery, called the aorta. The blood then goes to the rest of the body. .Assessment of the size, mass, geometry, and function of the left ventricle is fundamental for the diagnosis and prognosis of most cardiac diseases, including coronary artery disease, heart . Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the central measure of left ventricular systolic function. LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in .
why is left ventricle thicker
LV GLS is useful to detect future cardiotoxicity among patients receiving cardiotoxic chemotherapy, and to detect subclinical LV systolic dysfunction among family .
what is the function and anatomy of left ventricle
Buy Sid Meier's Civilization IV: The Complete Edition. $29.99. Add to Cart. See all. Includes 4 items: Civilization IV: Beyond the Sword, Civilization IV®: Warlords, Sid Meier's Civilization IV: Colonization, Sid Meier's Civilization® IV.
lv function of heart|what is the function and anatomy of left ventricle