lv longitudinal strain | time to peak longitudinal strain lv longitudinal strain Left ventricular (LV) global longitudinal strain (GLS) is a measure of the active shortening of the LV in the longitudinal direction, which can be assessed with speckle-tracking . 161,355. Three willows are located next to Draynor bank. A full load of 28 takes approximately 120 seconds at 90+ Woodcutting. Cutting willows is also one of the fastest ways to train Woodcutting in f2p (cutting maple logs or yew logs may be slightly faster [2], but these cannot be stored in any f2p wood boxes).
0 · time to peak longitudinal strain
1 · reduced global longitudinal strain
2 · longitudinal strain maps from echocardiogram
3 · global longitudinal strain treatment
4 · global longitudinal strain prognosis
5 · global longitudinal strain chart
6 · Lv strain normal values
7 · Lv strain echo normal values
Left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy is an independent cardiovascular risk factor associated with significant excess and morbidity and mortality rates. 1–3 There is now evidence for the effectiveness of antihypertensive agents, particularly ACE inhibitors, in reducing LV mass, 4–6 and this reduction in LV mass appears to carry a favorable prognosis.
Learn how to assess echocardiographic global longitudinal strain (GLS) for left ventricular (LV) systolic dysfunction. GLS is a simple parameter that expresses longitudinal shortening as a percentage, but it varies with age, sex, and LV loading conditions.Learn how to measure and interpret left ventricular (LV) systolic function using ejection fracti. Left ventricular (LV) global longitudinal strain (GLS) is a measure of the active shortening of the LV in the longitudinal direction, which can be assessed with speckle-tracking . Cardiovascular disease remains a leading cause of death and disability, responsible for 31% of all deaths. 1 Global longitudinal strain (GLS), assessed by 2-dimensional speckle .
This article reviews how to measure LV global longitudinal strain (LV GLS) by speckle tracking echocardiography and its role in assessing LV systolic function. LV GLS is an .This article reviews the conventional and contemporary echocardiographic techniques to evaluate LV systolic function, including speckle-tracking .
However, recent data have demonstrated that LV global longitudinal strain is a more sensitive marker for systolic dysfunction and provides incremental prognostic information in . Learn how to measure and interpret left ventricular (LV) systolic function using ejection fraction (EF) and myocardial strain. Find out how strain analysis can improve .

Normal global circumferential strain varied from -20.9% to -27.8% (mean, -23.3%; 95% CI, -24.6% to -22.1%). Global radial strain ranged from 35.1% to 59.0% (mean, 47.3%; 95% CI, 43.6% to .Global longitudinal strain (GLS) has emerged as a fine-tuned, highly reproducible, and operator-friendly method for quantification of left ventricular function and prognostication in a wide . LV global longitudinal strain (GLS) permits quantification of active myocardial deformation in the longitudinal direction, which is a more robust marker of LV performance than LVEF. 14 Moreover, LV GLS relates to the .
Learn how to assess echocardiographic global longitudinal strain (GLS) for left ventricular (LV) systolic dysfunction. GLS is a simple parameter that expresses longitudinal shortening as a percentage, but it varies with age, sex, and LV loading conditions. Left ventricular (LV) global longitudinal strain (GLS) is a measure of the active shortening of the LV in the longitudinal direction, which can be assessed with speckle-tracking echocardiography. Cardiovascular disease remains a leading cause of death and disability, responsible for 31% of all deaths. 1 Global longitudinal strain (GLS), assessed by 2-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography, has emerged as a new method for assessing left ventricular (LV) function. 2 GLS is altered despite preserved LV function as assessed by .
This article reviews how to measure LV global longitudinal strain (LV GLS) by speckle tracking echocardiography and its role in assessing LV systolic function. LV GLS is an earlier marker of LV dysfunction than LVEF and has prognostic value in various cardiac conditions.This article reviews the conventional and contemporary echocardiographic techniques to evaluate LV systolic function, including speckle-tracking echocardiography (STE). STE can detect subclinical LV dysfunction and predict cardiac outcomes for .
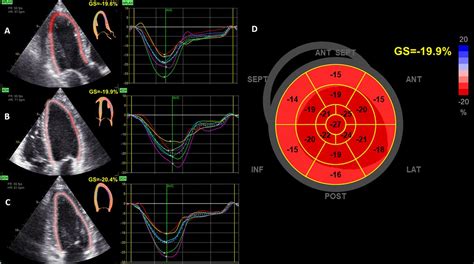
However, recent data have demonstrated that LV global longitudinal strain is a more sensitive marker for systolic dysfunction and provides incremental prognostic information in patients with severe AS when compared with LV ejection fraction.
Learn how to measure and interpret left ventricular (LV) systolic function using ejection fraction (EF) and myocardial strain. Find out how strain analysis can improve diagnosis and management of heart failure, valvular disease, and cardiotoxicity.Normal global circumferential strain varied from -20.9% to -27.8% (mean, -23.3%; 95% CI, -24.6% to -22.1%). Global radial strain ranged from 35.1% to 59.0% (mean, 47.3%; 95% CI, 43.6% to 51.0%). There was significant between-study heterogeneity and inconsistency.Global longitudinal strain (GLS) has emerged as a fine-tuned, highly reproducible, and operator-friendly method for quantification of left ventricular function and prognostication in a wide spectrum of cardiac diseases (3).
time to peak longitudinal strain
LV global longitudinal strain (GLS) permits quantification of active myocardial deformation in the longitudinal direction, which is a more robust marker of LV performance than LVEF. 14 Moreover, LV GLS relates to the extent of myocardial fibrosis in patients with severe AS 15 and is a strong prognostic marker in patients with severe AS. 16, 17 .
Learn how to assess echocardiographic global longitudinal strain (GLS) for left ventricular (LV) systolic dysfunction. GLS is a simple parameter that expresses longitudinal shortening as a percentage, but it varies with age, sex, and LV loading conditions. Left ventricular (LV) global longitudinal strain (GLS) is a measure of the active shortening of the LV in the longitudinal direction, which can be assessed with speckle-tracking echocardiography. Cardiovascular disease remains a leading cause of death and disability, responsible for 31% of all deaths. 1 Global longitudinal strain (GLS), assessed by 2-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography, has emerged as a new method for assessing left ventricular (LV) function. 2 GLS is altered despite preserved LV function as assessed by .
This article reviews how to measure LV global longitudinal strain (LV GLS) by speckle tracking echocardiography and its role in assessing LV systolic function. LV GLS is an earlier marker of LV dysfunction than LVEF and has prognostic value in various cardiac conditions.
This article reviews the conventional and contemporary echocardiographic techniques to evaluate LV systolic function, including speckle-tracking echocardiography (STE). STE can detect subclinical LV dysfunction and predict cardiac outcomes for . However, recent data have demonstrated that LV global longitudinal strain is a more sensitive marker for systolic dysfunction and provides incremental prognostic information in patients with severe AS when compared with LV ejection fraction. Learn how to measure and interpret left ventricular (LV) systolic function using ejection fraction (EF) and myocardial strain. Find out how strain analysis can improve diagnosis and management of heart failure, valvular disease, and cardiotoxicity.Normal global circumferential strain varied from -20.9% to -27.8% (mean, -23.3%; 95% CI, -24.6% to -22.1%). Global radial strain ranged from 35.1% to 59.0% (mean, 47.3%; 95% CI, 43.6% to 51.0%). There was significant between-study heterogeneity and inconsistency.
Global longitudinal strain (GLS) has emerged as a fine-tuned, highly reproducible, and operator-friendly method for quantification of left ventricular function and prognostication in a wide spectrum of cardiac diseases (3).
reduced global longitudinal strain

Search Cucina jobs in Las Vegas, NV with company ratings & salaries. 10 open jobs for Cucina in Las Vegas.
lv longitudinal strain|time to peak longitudinal strain