lv venting ecmo | central vs peripheral va ecmo lv venting ecmo Percutaneous trans-aortic LV assist device Impella ® combined with VA ECMO. . Dooors 2 Level 22 Walkthrough. You can watch all the walk through videos of Dooors 2 here http://gunzarsenal.com/category/dooors-2-room-escape/.
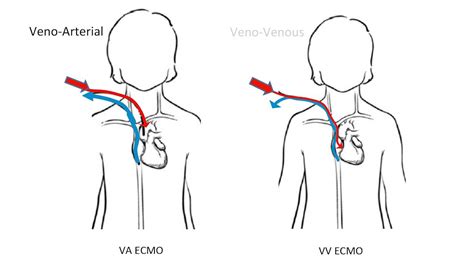
0 · what is vva ecmo
1 · vv ecmo location
2 · va ecmo vs impella
3 · va ecmo lv distention
4 · lv unloading in va ecmo
5 · impella device vs ecmo
6 · ecmo left ventricular unloading
7 · central vs peripheral va ecmo
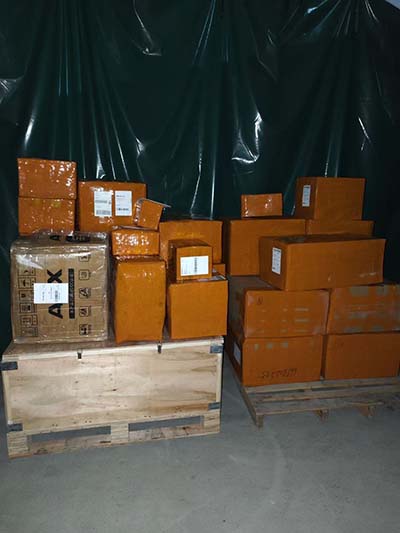
67387284. [email protected]. Whatsapp: 67387284. For DPD Pickup point questions. 00:00-24:00. 67387282. For media, cooperation offers. [email protected]. Shipment receiving branch working hours. Uriekstes 8a, Riga. Weekdays: 09.00 to 17.30. Arrival only by prior arrangement here. Sales department. 67387286. [email protected]. Order submission line. .
what is vva ecmo
shalonda lewis henrico rolex watches
vv ecmo location
Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA ECMO) is an established method of short-term mechanical support for patients in cardiogenic shock, but can create left ventricular .Percutaneous trans-aortic LV assist device Impella ® combined with VA ECMO. . Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO) is a mechanical circulatory support (MCS) strategy that provides extracorporeal blood flow of 4 to 6 L/min and sufficient gas exchange to support systemic .
Surgical LV vent. Surgical Technique – insertion of apical left ventricular vent. by Prof David McGiffin. Preparation. The patient is placed with a 30-degree bump on the left side. The . The study by Al-Fares et al 5 now highlights the need for specific algorithms to optimize LV venting with VA-ECMO. In this analysis, intraaortic balloon pump was the most . LV venting during VA-ECLS is significantly associated with improved weaning from ECLS and reduced short-term mortality in adults with cardiogenic shock, especially if .
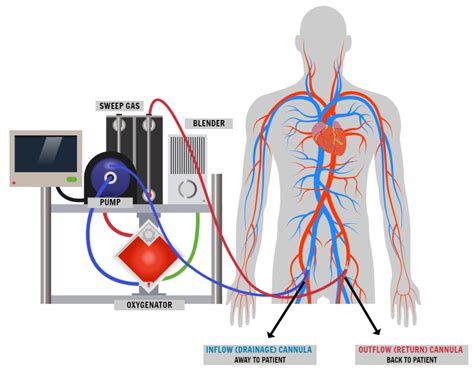
Peripheral cannulation for VA-ECMO results in retrograde flow to the proximal aorta and substantial increase in left ventricular (LV) afterload, often leading to increased LV end .One such debate relates to the need for and the optimal timing and type of a left ventricular (LV) venting strategy to counteract the potential overloading effects on the left ventricle that can .
rolex watch usa address
In a recent paper in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, Grandin et al 1 reported that mechanical unloading of the left ventricle (LV) during peripheral venoarterial . Percutaneous trans-aortic LV assist device Impella ® combined with VA ECMO. The Impella ® (Abiomed, Danvers, MA) is a trans-aortic LV assist device designed as a . Several options exist for management of LV distention during VA-ECMO, such as an IABP, a percutaneous left atrial (LA) or LV vent, an open surgical LV vent, a percutaneous .Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA ECMO) is an established method of short-term mechanical support for patients in cardiogenic shock, but can create left ventricular (LV) distension. This paper analyzes the physiologic basis of .
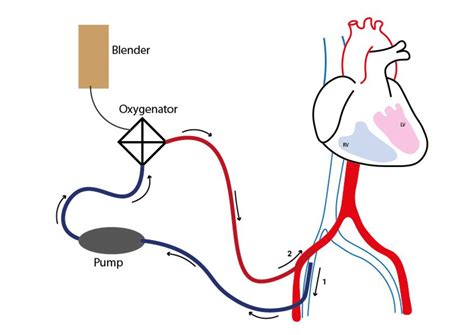
Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO) is a mechanical circulatory support (MCS) strategy that provides extracorporeal blood flow of 4 to 6 L/min and sufficient gas exchange to support systemic perfusion in severe cardiorespiratory failure.Surgical LV vent. Surgical Technique – insertion of apical left ventricular vent. by Prof David McGiffin. Preparation. The patient is placed with a 30-degree bump on the left side. The incision is a short left anterolateral thoracotomy with the interspace determined by the size of the heart. The study by Al-Fares et al 5 now highlights the need for specific algorithms to optimize LV venting with VA-ECMO. In this analysis, intraaortic balloon pump was the most common venting strategy and was associated with improved outcomes.
LV venting during VA-ECLS is significantly associated with improved weaning from ECLS and reduced short-term mortality in adults with cardiogenic shock, especially if implemented early (within 12 hours).
Peripheral cannulation for VA-ECMO results in retrograde flow to the proximal aorta and substantial increase in left ventricular (LV) afterload, often leading to increased LV end-diastolic pressure and decreased stroke volume. 1 This phenomenon of LV distention can result in pulmonary edema, thrombus formation in the left heart due to stasis .
One such debate relates to the need for and the optimal timing and type of a left ventricular (LV) venting strategy to counteract the potential overloading effects on the left ventricle that can occur during VA ECMO support.
In a recent paper in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, Grandin et al 1 reported that mechanical unloading of the left ventricle (LV) during peripheral venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is associated with lower mortality.
Percutaneous trans-aortic LV assist device Impella ® combined with VA ECMO. The Impella ® (Abiomed, Danvers, MA) is a trans-aortic LV assist device designed as a catheter-based, micro-axial impeller pump that provides continuous blood flow from the LV into the ascending aorta. Several options exist for management of LV distention during VA-ECMO, such as an IABP, a percutaneous left atrial (LA) or LV vent, an open surgical LV vent, a percutaneous endovascular left ventricular assist device (LVAD), and a nondischargeable surgically implanted left ventricular assist device. 2 Current ECMO guidelines do not recommend any .Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA ECMO) is an established method of short-term mechanical support for patients in cardiogenic shock, but can create left ventricular (LV) distension. This paper analyzes the physiologic basis of . Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO) is a mechanical circulatory support (MCS) strategy that provides extracorporeal blood flow of 4 to 6 L/min and sufficient gas exchange to support systemic perfusion in severe cardiorespiratory failure.
Surgical LV vent. Surgical Technique – insertion of apical left ventricular vent. by Prof David McGiffin. Preparation. The patient is placed with a 30-degree bump on the left side. The incision is a short left anterolateral thoracotomy with the interspace determined by the size of the heart.
The study by Al-Fares et al 5 now highlights the need for specific algorithms to optimize LV venting with VA-ECMO. In this analysis, intraaortic balloon pump was the most common venting strategy and was associated with improved outcomes. LV venting during VA-ECLS is significantly associated with improved weaning from ECLS and reduced short-term mortality in adults with cardiogenic shock, especially if implemented early (within 12 hours).Peripheral cannulation for VA-ECMO results in retrograde flow to the proximal aorta and substantial increase in left ventricular (LV) afterload, often leading to increased LV end-diastolic pressure and decreased stroke volume. 1 This phenomenon of LV distention can result in pulmonary edema, thrombus formation in the left heart due to stasis .
One such debate relates to the need for and the optimal timing and type of a left ventricular (LV) venting strategy to counteract the potential overloading effects on the left ventricle that can occur during VA ECMO support.In a recent paper in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, Grandin et al 1 reported that mechanical unloading of the left ventricle (LV) during peripheral venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is associated with lower mortality.
Percutaneous trans-aortic LV assist device Impella ® combined with VA ECMO. The Impella ® (Abiomed, Danvers, MA) is a trans-aortic LV assist device designed as a catheter-based, micro-axial impeller pump that provides continuous blood flow from the LV into the ascending aorta.
Douglas dāvanu karte ir ideāla dāvana, kas paver durvis uz skaistuma pasauli gan viņai, gan viņam! 2 bezmaksas paraugi Bezmaksas piegāde no 39.95 EUR
lv venting ecmo|central vs peripheral va ecmo